15 July 2015 has been declared as the World Youth Skills day for the first time ever. To commensurate this day, Hon’ble Prime Minster shri. Narendra Modi launched the Skill India Campaign. This is India’s first integrated national scheme for developing skills and promoting entrepreneurship at a broader scale.

Based on the vision of Skill India Programme, Bharat Sevak Samaj, National Development Agency constituted by the Indian Parliament in 1952, promotes a mission movement called National Skill India Mission(Nsim).
Hon'ble advisor of Bureau of Parliamentary Studies and Training (BPST) Lok sabha, Govt. of India, Shri. RAGHUNANDAN SHARMA's recommondations for National Skill India Mission is as follows:












- Bridging the gap for employment generation
- Reducing Poverty
- Enhancing Competitiveness of Indian Business
- Preparing the youth of India as a manpower resource for World Markets
- Diversifying Skills development programmes to meet the changing requirements, particularly of emerging knowledge economy.
- Ensuring quality and relevance of training
- Building true market place competencies rather than mere qualifications.
- Providing opportunities for life-long learning for skill development.
- Promoting greater and active involvement of social partners and forging a strong, symbiotic, public-private partnership in skills development.
- Mobilizing adequate investments for financing skills development sustainable.


“To provide training and skill development to the youth of our country covering each and every village/city and to empower all individuals through improved skills, knowledge and employment opportunities”.
- Skills development system which supports employment generation, economic growth and social development processes.
- Skills development system which supports diversity while maintaining national coherence.
- Skills development system based on strong public private partnership in training and assessment of unskilled youths.
- Skills development system responds to technological change, employment requirements and improvements in the productivity and competitiveness of industry.
- Skills development system which supports to achieve inclusive growth by providing equal access to training to all, and responds to the needs of the unorganized sector.
- Skills development system in which qualifications and certification are quality assured and recognized nationally, across organizations, as well as internationally.
- Skills development system which promotes lifelong learning and the continuous upgrading of the skills and knowledge.
- Skills development system supported by suitable funding.
- The emphasis is to skill the youths in such a way so that they get employment and opportunity to improve entrepreneurship and ability to adapt to changing technologies and labour market demands.
- Provide training , support and guidance for all occupations that are of traditional type like carpenters, cobblers, welders, blacksmiths, masons, nurses, tailors, weavers etc.
- More emphasis will be given on new areas like real estate, construction, transportation, textile, gem industry, jewellery and designing, banking, tourism and various other sectors, where skill development is inadequate or absent.
- To create a hallmark called ‘Rural India Skill’, so as to standardize and certify the training process.
- Strengthening productivity, competitiveness and supporting the process of economic growth.
- Creating employment opportunities by attracting business expansion on the substrate of availability of relevant skills.
- Tailor-made, need-based programmes would be initiated for specific age groups which can be like language and communication skills, life style and positive thinking skills, personality development skills, management skills, behavioural skills including job and employability skills.
- The course methodology of Nsim would be innovative, which would include games, group discussions, brainstorming sessions, practical experiences, case studies etc.
‘Recognition of Prior Learning’ or ‘RPL’ is the process of recognizing previous learning towards gaining a qualification. In India 25/100 are getting skill training through informal way, by learning by doing concept. National Skill India Mission is planning to recognize these skills, through skill knowledge provider or through N-sim skill training institutes and planning to help the learner to bridge their skill with formal skill education. Certificates from formal skill education empowers them to set vertical/horizontal mobility in their career.
As estimated by the Govt of India, approximately 93% of the country’s workforce is in the unorganized sector. People from the unorganized sector acquire ‘skills’ through practice, which needs refinement to reach more levels. Recognition by Prior Learning (RPL) is an appropriate method of assessment that considers whether the candidate can meet the assessment requirements of competencies that they already possess. Valuing and recognizing these learning outcomes may significantly improve the self-esteem and well being of the individuals, motivate them to further their learning and strengthen their labour markets opportunities.
Recognition of Prior Learning as a tool in the Development of India
As per the Nsim vision recognition of prior Learning enables effectiveand maximum utilization of human resources and can be considered as a ‘Tool’. 93 percentage of the workforce in India acquired their skills at the workplace as on- the-job training. Persons trained this way earn low wages, despite being fully skilled and are often exploited by the employers since they do not have any formal certificate. RPL has the potential to be a powerful tool in the development of India and in the implementation of the Reconstruction and Development Programme. As per the study conducted by Nsim, RPL is seen to have the capacity to contribute to redress equity by opening up more ways for people to attain qualified status. It could:
- Enable more people to reach higher levels of qualification and expertise by beginning with an acknowledgment of existing skills and knowledge.
- Contribute to enhancing international economic competiveness by building an often invisible and unacknowledged workforce skills.
- Often the first step in attaining the goals of developing a multi-skilled and flexible workforce by acting as an audacious tool to quality existing competence.
Broader Aims
- The idea is to raise confidence, improve productivity and give proper direction through skill assessments and certification of the unorganized sector, to enable them to get blue-collar jobs.
- Assessment of existing skills of the unorganized sector is very essential to channelize them for proper job opportunities
- Every job aspirant would be treated with equal importance and would be given training in soft skills.
- Nsim’s vision is to improve the physical and mental development of the youths of the country so that none of them remains unemployed and the country’s unemployment problem also gets reduced.
Target people are the following
- Youths without skills
- Youths with non-formal skills
- Youths with in-formal skills
- All private/government institutions being infrastructure for skilltraining
- All skilled persons, who has the capacity to train the unskilled person/informally skilled person /non-formally skilled person.
- All industrial/service establishments, who are in need of skilled persons.
- Overseas Establishments, looking for skilled persons
- Recruitment Agencies
- Placement Agencies
Targets for next 5 years
- The National Skillindia Mission will promote, converge, implement and monitor skill development activities across the country.
- N sim aims at providing training on skill development to 50 millions youths in the country with in 2022.
- Over the next 5 years, Nsim aims at certifying 50 millions youthsunder the RPL.
- N sim aims to develop skill knowledge providers across India, to train the youth as per the international standards in the coming years.
- After ‘Digital India’ and ‘Make in India’, the Union Government launched ‘Skill India’, which is supposed to be a multi-skill programme. Like all other programmes, ‘Skill India’ too is a dream project of Hon’ble Prime Minister of India. Based on the recommendations of Skill India Programme Bharat Sevak Samaj, the National Development Agency announces National Skill India Mission (N-sim).
- Skills and knowledge are the driving forces of economic growth and social development for any country. Countries with higher and better levels of skills adjust more effectively to the challenges and opportunities in the world of work.
- As India moves progressively towards becoming a ‘knowledge economy’it becomes increasingly important that the country should focus on advancement of skills and these skills have to be relevant to the emerging economic environment.
- In order to achieve the twin targets of economic growth and inclusive development, India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP)has to grow consistently at 8% to 9% per Ann-um. This requires significant progress in several areas, including infrastructure development, agricultural growth coupled with productivity improvements, financial sector growth, and a healthy business environment, ably supported by a skilled workforce.
- Skill development is one of the essential ingredients for India’s future economic growth as the country transforms into a diversified and internationally-competitive economy. Skill development is going to be the defining element in India’s growth story. Firstly, we need to re-define the relationship of education, employment and skills development. Secondly, as a very large population, India would never be able to upskill all of its youth across the country through the conventional education framework.
- Government systems alone cannot accomplish this task. It calls for a concerned effort of government systems, private players and NGOs to address the issue in a comprehensive manner. If India is to gain its rightful place in the world, reap equal benefits and opportunities for all and rise from the debris of poverty and several other pressing issues, skills development will require to be given a place right on top of national priorities.
- India is uniquely positioned to fill the gap of the industry demand globally with its youth power. What Mechanical Revolution did to the European economy in the 50s and Oil Revolution did to Middle East economy in the 70s, the skilled manpower revolution can do the same to the Indian economy, provided we are able to gauge and see the exact requirement of the industry globally and are able to train and certify our students to a level which is accepted by global standards.
- The accelerated economic growth has increased the demand for skilled manpower that has highlighted the shortage of skilled manpower in the country. The lack of available applicants, shortage of hard skills and shortage of suitable employability, including soft skills, are some of the key reasons in finding a suitable candidate for available jobs in the country.
- As compared to western economies where there is a burden of an ageing population, India has a unique 20-25 years window of opportunity called the “demographic dividend”. This “demographic dividend” means that as compared to other large developing and developed countries, India has a higher proportion of working age population vis-à-vis its entire population.
- In this Twelfth Five Year Plan, India has set a tough challenge in the field of Skill education and training in its approach paper. It aims to increase the percentage of workforce with formal skills to 25% at the end of the plan. It is estimated that 50-70 million jobs will be created in India over the next five years and about 75% -90% of these additional employment avenues will require some Skill training.
The well articulated policies of the N-SIM to leverage skill training and to make the skill training capabilities of India as a vehicle to propel itself as a strong skilled super power in the coming years are also very well discussed in the N-SIM implementation process.
In order to achieve the project goals, the need of the hour is a highly pro active role that would take into account the changing scenarios in the Skill Education and the non-linear interactions between the forcing functions.
(a) Skilled Youth
India has the second largest pool of English speaking scientific manpower in the world today. Of this, more than 3 million were skilled professionals. This pool of young skilled professionals, could be used as trainers to train the unskilled youth of India through N-sim training institutions. N-sim will take steps to reduce the gap between the skilled and unskilled, through creating solutions that enable everyone to participate in the skill India movement.
(b) Private -public partnership in Skill India training institution
N-sim, will promote maximization of usage of infrastructure available in India to train the unskilled with the help of private and public establishments. An amicable revenue sharing methodology would be worked out, between parties for the smooth implementation. There are 3 basic constituters that shape the skill training. These are infrastructure, trainers and training content. Together, these generate skilled workforce. N-sim by virtue of its having a large pool of skilled talent and being established by one of the pioneer organization (Bharat Sevak Samaj), is excellently poised to generate original training content.
The role of private sector players can be categorized as
- Academic Partners
- Industrial Partner
- NGO’s and other local Stake holders
- University, industry linkage as per UGC norms.
Skilled Knowledge Provider
N-sim Skill India programme will be implemented through skill knowledge provider(SKP). Skill knowledge provider means someone who trains, instructs, teaches or otherwise enables the learner(s) to acquire the appropriate knowledge and skills. Skill knowledge provider will be R & D institutes, training institutes, individual, universities etc.
The relationship between quality of skill training and quality of Skill Assessment is important to place the quality assurance of skill training of National Skill India Mission. A National Assessment system should underpin National Skill India Mission’s, Skill India Programme. The overall purpose of quality assurance of the National Skill India Mission, can take place only through, quality assessment as follows
- Continuous and comprehensive evaluation of skill training institutes
- Third party assessment of the skilled person, after the training programme
- All certificates should show the level of the training programme as per the recommendation of National Skill Qualification Frame Work.
- Certificates have a clear purpose and a relationship to one another.
- The requirements for certificates are stated explicitly, based on theNational Skill Qualification Frame - work.
- Certificates have credibility with learners, employers, providers,professional bodies.
- Certificates provide opportunities for vertical and horizontal progression and mobility.
- All need based courses will be selected based on National Skill Qualification Frame work (NSQF).
- Assessors training programme will be organized as per the NSQF norms.
Learning towards skill certificate from National Skill India Mission may be gained in a number of contexts
- Higher Education institution provision (Short course, under graduate and post graduate)
- Higher level skill qualification
- Certificates for professional bodies
- Employer in –house education and training provision
- Learning from experience
On 19th December 2013, the cabinet committee on skill development approved the National Skills Qualifications Frame Work (NSQF), a quality assurance framework which organizes qualification according to a series of levels of knowledge skills and aptitude. These levels are defined in terms of learning outcomes which the learner must possess, regardless of whether they are acquired through formal, non-formal or informal learning.
National Skill India Mission (Nsim) would give in-service model training to all skill knowledge providers in consultation with industry on a continuous and comprehensive training module. The training programme will be conducted every 6 months for all SKP’s in every year.
- The skills to be offered would be dictated always by the labour market research and needs analysis of industry. This would also lead to the development of the Labour Markets Information System(LMIS). Industry would have an important role in defining skills and competencies required for each occupation within their respective industry/sector with in the NOS developed.
- Industry participation should be encouraged at all levels such as curricula design and specifying needs for various job roles, on job training for students, contribution by way of requirement, production oriented labs, research labs etc, internships, apprenticeship and placements for students participation in teacher/ assessor training and skill up gradation.
- The sector wise skill research programme should be headed by competent professional, with a deep understanding of various problems and issues in curriculam making, teaching –learning methodology, contemporary advances in cognitive as well as skill learning and all such related matters.
- The research division of N-sim needs to be properly staffed. In order to achieve this objective, it has to be ensured that people well-versed in research and also conversant with the realities of the field situation are located and placed to the division.
- The research division may undertake analysis of examination date, pupils performance with a view to market reality.
- The sector wise research division may undertake analysis of market demand and report the same to N-sim Head Office on every month.
- The sector wise research division should conduct survey of the students placed after training from N-sim to get their original potential when placed in real life.
For India to reap the demographic dividend, it is very important to develop ‘employable Skills’ among our youth. With over 15 crore youth in the 18-23 age group, India has a daunting challenge to meet the human development and Learning needs of this large group. By recognizing prior Learning and by linking mobility in mastery of skills with pursuit of knowledge through the formal education stream, the Skill Assessment Matrix is a very important felt need. This Skill Assessment Matrix, aimed at promoting lateral and vertical mobility, is an effort to integrate skill and main stream general Education. N-sim will Constitute Expert Committee on Skill Assessment Matrix, to connect the programme with general education.
Nsim will take initiative to start Research institutes, in all sectors with the help of industries and universities to strengthen, the skilling process. Nsim Sector Development Council will work in collaboration with Universities, Industries, Employment Agencies, Training institutes, Govt Agencies to find out the market need and the skills needed to satisfy the market in a time-bound manner.
National Skill India Mission (Nsim) will use the services of skilled individuals, with/with out qualifications, graduates with skills, professionals from Engineering, Teaching, Media and Entertainment, Industry. They will be called as Accreditation Skill Teacher. Thus Nsim will act as the common platform for all to share their skill with unskilled.
A Massive Open Online Course (MOOC) is a model for delivering learning content online to any person who wants to take a course, with no time limit on attendance.
- Nsim’s Massive Open Online Course (MOOC) was designed to create an option for remedial Teaching – which helps the students to build their skills before and after Training period, and thus reduce the Remedial Teaching in the class room.
- Nsim’s Massive Open Online Course (MOOC) helps the students to better their understanding through the vast collection of data for Completion, Motivation and Learning of their skills.
- Nsim MOOC provides inter- active user forums to support community interactions between students.
Nsim’s researched and revolutionary design of the skills training modules gives emphasis on productivity, positivity and success of individual. The self realization and confidence building propels people to set and achieve goals that leads to growth of the person, the family and ultimately the society/ Nation.
The key elements of Nsim’s training module are:
- It helps the learner to become a confident presenter in all the fields. Nsim helps the learner to become a successful presenter in every meeting, every one-to-one, every time the learner speaks to others, whether the meeting is formal or informal.
- Nsim training module helps the learner to correct their Body language that helps the learner to improve their communication and personal impact and this makes a positive impression on others. The learner can read and understand people by observing their body language. It helps the learner to build relationships and become more influencial.
- Nsim MOOC provides inter- active user forums to support community interactions between students.
- Prior Learning assessment and recognition can take various forms and outcomes can be used for a large number of purposes relevant to the goals of individuals, labour market partners and society at large.
- Will enable millions to gain livelihoods and take our country ahead in its path towards inclusive and sustainable growth.
- Skills recognition and certification initiatives of Nsim in the informal sector will provide an important path way for the 90 percent of Indians who work in the un-organized sector.
- Unorganized people from wool sector will be identified with the help of Wools Development Corporations of state Governments. As a first step, in Karnataka with the support of 600 wools societies under Karnataka Wools Corporation, RPL and skill upgradation will be done.
- As a joint venture with ‘SMILE’ the NGO works in the slum, skilled people from slums of Mumbai will be identified, and certified. Identification and nurturing of skills in slums will be one of the key areas.
- AS a joint venture with National Film Development Corporation, Govt. of India skilled persons without certification will be identified and certified. Media and entertainment sector is one of the primary target of Nsim.
- The existing skill knowledge providers of Nsim spread across India will be used to identify and certify the unskilled in the Building, Plumbing, Constructions and various sectors.
- Nsim Skill Knowledge Provider will be set up across India, to enable a lifelong learning society in which learners will be enabled to take up learning opportunities at chosen stages throughout their lives.
- With the help of skill knowledge provider digital skill will be imparted to the mass which lies at the bottom of pyramid. Expected outcome from this sector will be 50 millions in the coming 5 years.
- In collaboration with Career Development Centres (CDC) and Career Placement Cell (CPC) of Visweswarayya technological University, Banglore, Nsim will start 25 market based courses as per the NSQF norms.
- In collaboration with Karnataka Vocational Training and Skill Development Corporation Limited, Nsim plans to recognize the unorganized skilled people of Karnataka through a joint certification programme to bridge them to formal education structure.
- With the help of Kudumbasree Movement, the poverty allevation programme of Govt. of Kerala, Nsim plans to conduct entrepreneurship programme to the youths to strengthen the Make- in-India programme announced by the Union Govt.
Priority Sector
BPST, Reviewed the National Skill India Mission constituted by the Bharat Sevak Samaj and appreciated the Mission Movement to strengthen the Skill India, Digital India, Make-in-India and Stand-up-India Programmes of Hon’ble Prime Minister Shri. Narendra Modi. BPST also recommends National Skill India Mission Government status in its operations for Skill India.
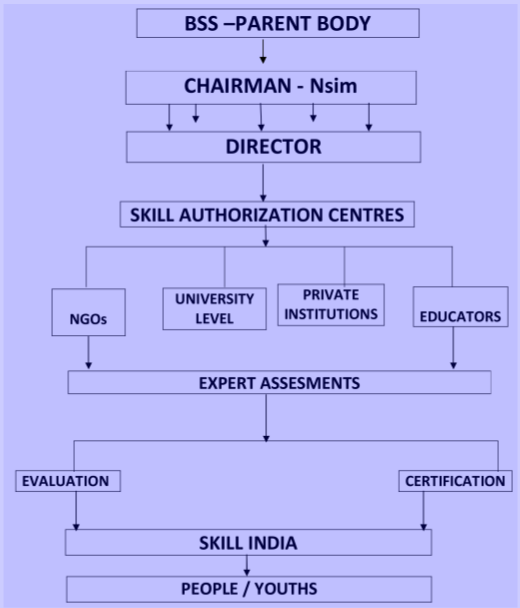
National Skill India Mission (Nsim) -
ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE