Stories you may like
RADIOLOGIST
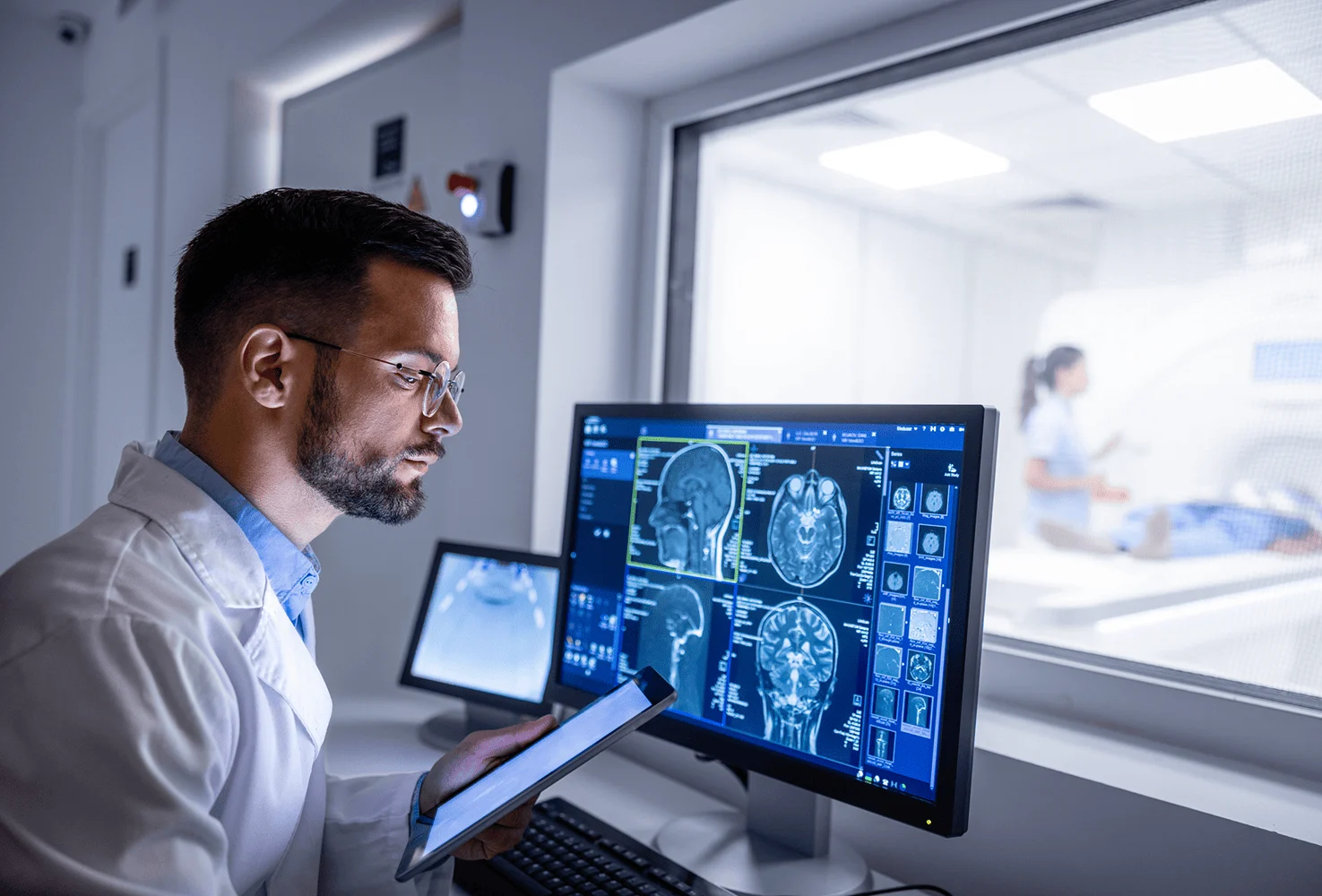
Radiology, also known as diagnostic imaging, is a series of tests that take pictures or images of parts of the body. The field encompasses two areas — diagnostic radiology and interventional radiology — that both use radiant energy to diagnose and treat diseases. While there are several different imaging exams, some of the most common include x-ray, MRI, ultrasound, CT scan and PET scan.
Who is the radiologist?
A radiologist is a medical doctor (MD) or a Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO) who has finished a 4-year residency in radiology. They often act as a consultant to another healthcare provider who is caring for the patient. Or they may be the patient's primary provider in treating a disease
After their residency, most radiologists become board-certified. This may be done by the American Board of Radiology (for an MD). Or by the American Osteopathic Board of Radiology (for a DO). Some go right into practice. But radiology has become a very specialized field. So others begin fellowship programs for more training to focus on a specialty area, such as:
-
Neuroradiology. Focuses on the central nervous system, head, neck, and spine.
-
Pediatric radiology. Focuses on ways to create images of children's bodies, their organs, and internal structures.
-
Breast imaging. Focuses on diagnosing breast diseases.
-
Cardiovascular radiology. Focuses on diagnosing diseases of the heart and blood vessels. This includes the arteries and veins.
-
Chest radiology. Focuses on diagnosing and treating the chest, specifically the heart and lungs.
-
Gastrointestinal radiology. Focuses on diagnosing and treating the digestive tract.
-
Genitourinary radiology. Focuses on diagnosing and treating the organs of the reproductive and urinary tracts.
-
Musculoskeletal radiology. Focuses on diseases of the muscles and skeleton.
-
Emergency radiology. Focuses on diagnosis of trauma and nontraumatic emergency conditions.
-
Interventional radiology. A subspecialty of radiology. It focuses on diagnosing and treating patients by using minimally invasive interventional methods. These include imaging and treatment of blood vessels (angiography), biopsy procedures, line and tube placement, and fluid abscess drainage.
-
Nuclear radiology. A subspecialty of radiology. It focuses on diagnosing and treating people with tiny doses of radioactive material.
Radiation oncology uses radiation to treat cancer (and a few other diseases). Also uses imaging, such as CT scans and MRI, as aids in treatment planning and delivery of care.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Become a Radiologist in India
Step 1: Complete 10+2 with Science Stream
The first step begins after Class 10:
- Choose Science stream with Biology in Class 11 and 12.
- Score well in Physics, Chemistry, and Biology (PCB).
- English is also a compulsory subject.
Eligibility: Minimum 50% marks in PCB for general category and 40% for reserved categories.
Step 2: Qualify for NEET-UG Exam
To enter the medical field, you must clear the NEET-UG (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test).
- Conducted annually by NTA (National Testing Agency)
- Single national-level entrance exam for MBBS and BDS
- Minimum age: 17 years
Subjects Covered: Physics, Chemistry, Biology (Botany + Zoology)
A good NEET score will get you admission into MBBS, which is the base degree to become a radiologist.
Step 3: Complete MBBS (5.5 Years)
After clearing NEET, take admission into a recognized medical college for the MBBS course.
Duration: 4.5 years of academic study + 1-year internship
In MBBS, you’ll learn the basics of medicine, surgery, pathology, anatomy, and diagnostic techniques.
After completing your MBBS, you become a general physician, but to become a radiologist, you must specialize further.
Step 4: Prepare and Clear NEET-PG
After MBBS, you must qualify NEET-PG (Postgraduate) to enter into a specialty.
To become a radiologist, you need to take:
- MD (Doctor of Medicine) in Radiology OR
- DNB (Diplomate of National Board) in Radiology
NEET-PG is a national-level competitive exam with thousands of MBBS graduates competing for a few seats.
Tip: A high NEET-PG rank is required to get a radiology seat because it’s a top-choice branch.
Step 5: Pursue MD/DNB in Radiology (3 Years)
If you get a good NEET-PG score, you can pursue:
- MD Radiology from a medical college or university, OR
- DNB Radiology from a hospital or institute recognized by NBE
Both MD and DNB are considered equivalent by the Medical Council of India (now under NMC).
You’ll study advanced diagnostic imaging, radiographic anatomy, physics of radiology, and interventional procedures.
Step 6: Optional Super-Specialization – DM or Fellowships
Though not compulsory, many radiologists go for super-specialty or fellowship programs to gain more expertise.
Available options:
- DM (Doctorate in Medicine) in Interventional Radiology
- Fellowships in:
- Neuroradiology
- Musculoskeletal Radiology
- Pediatric Radiology
- Breast Imaging
- Onco-radiology
These help improve skills and salary, and open job opportunities in top hospitals.




User's Comments
No comments there.