Stories you may like
Radiographer
A radiographer is a health professional who performs diagnostic tests, including x-rays, computerised tomography (CT) scans, ultrasounds or magnetic resonance imaging to generate radiographs. Radiography is a procedure that uses radiation to record images, or radiographs, on a radiosensitive film. Other terms to describe this role include radiologic technologist and x-ray technician. Performing the role effectively requires technicians to possess a combination of skills and knowledge. They typically find employment in hospitals, diagnostic centres, medical laboratories and imaging centres, and work fixed shifts. Areas of specialisation include:
- Mobile radiography: This involves using mobile imaging equipment to perform tests in hospital wards or at the patient's home due to their medical issues.
- Trauma radiography: In this field, you specialise in imaging traumatic bone and joint injuries.
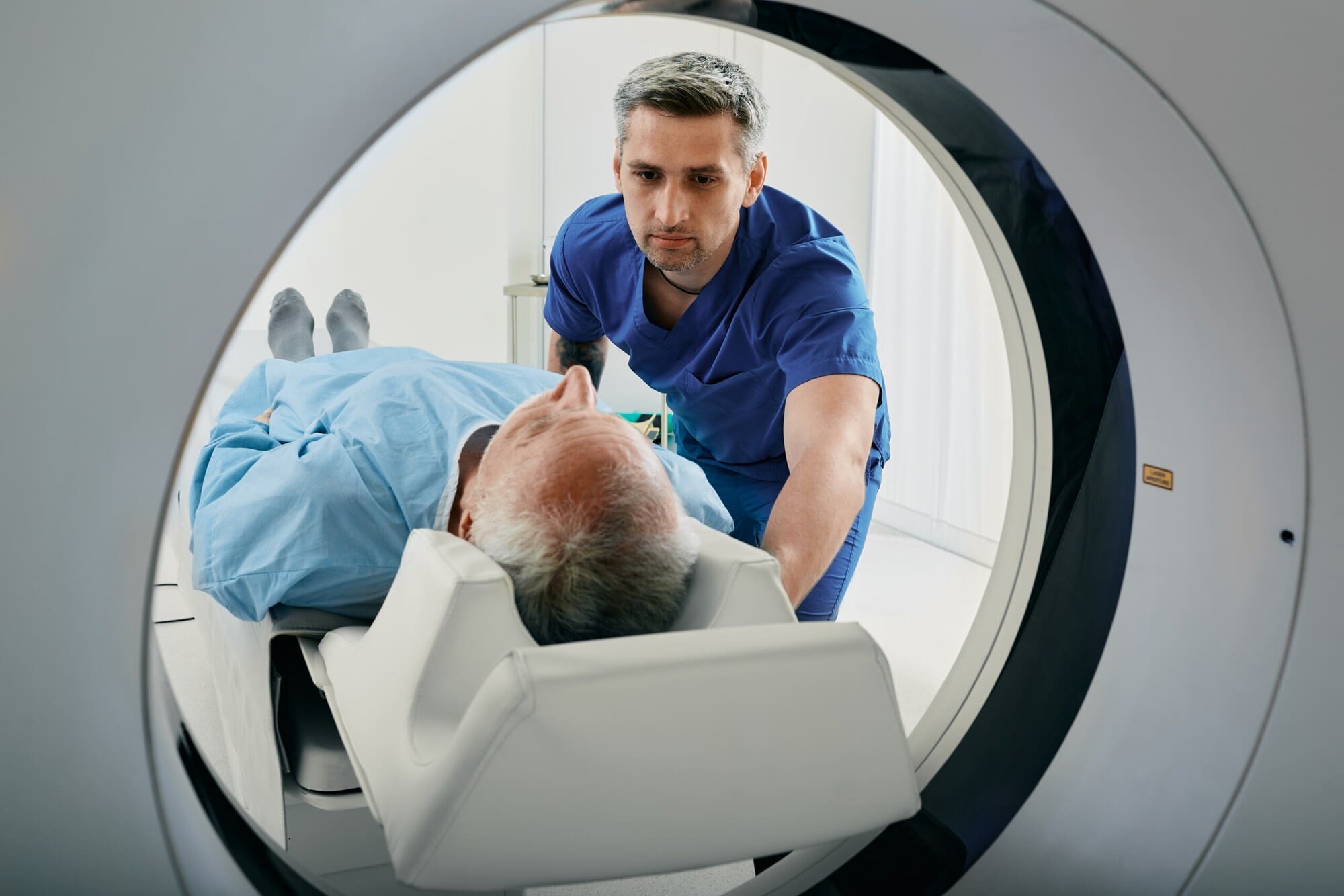
- Computed tomography: This involves using 3D x-ray tools to create detailed radiographs.
- Mammography: Mammography is a diagnostic and screening x-ray imaging technique used to examine the breasts. It is primarily used to detect breast cancer or other breast related diseases.
- Sonography: Sonography is a non-invasive technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce real-time images of soft tissues and internal organs, commonly used for purposes like monitoring fetal development.
- Diagnostic Radiography: It is a medical imaging technique that uses X-rays to create images of internal body structures to diagnose and treat illnesses and injuries.
- Fluoroscopy: Fluoroscopy is a medical imaging technique that uses X-rays to create real-time, continuous images of internal organs and tissues.
- Angiography: This involves the use of x-ray imaging to examine blood vessels.
What Does A Radiologic Technologist Do?
Here are some key duties of a radiologic technologist:
- Operate imaging machinery. X-ray technicians operate the high quality imaging machinery, position it correctly and monitor test progress. They perform tests such as CT scans, bone density scans, x-rays, fluoroscopies and cystograms.
- Develop digital imagery. Using imaging equipment, radiological technologists take pictures of a patient's internal organs per the doctor's instructions and record them. They ensure that the images are clear, accurate and complete to help the doctor make an accurate diagnosis.
- Assist patients and their family members. These technicians offer patient care to those undergoing a diagnostic test by outlining the process, answering questions and helping them to reposition or move. They also interact with people caring for the patient to offer support and explain any necessary actions before or after the test.
- Ensure patient safety. Medical imaging machines use a form of radiation to record images of internal organs, bones or joints to identify injuries. It is the duty of the x-ray technician to ensure that the radiation levels are within the acceptable exposure limits and that all necessary precautions are in place to ensure patient safety.
- Maintain machinery and clean the work area. These technicians are responsible for maintaining the machinery, cleaning it and sanitising different parts after each test. They also troubleshoot the imaging machine when it malfunctions and liaise with the service provider to ensure timely maintenance.
- Document patient history and records. Medical technicians usually collect information, such as the patient's medical history and personal details, before conducting a diagnostic test. They also share relevant data with other departments, such as the billing and medical record-keeping teams.
Radiography Skills
Here are some skills that can help you perform the role of radiological technologist effectively:
- Examination abilities: The examination process includes collecting patient details, explaining the test to patients, positioning patients appropriately, ensuring their safety, completing the scan and recording it. Examination skills, such as observation, problem-solving and analytical skills, help you perform tests accurately.
- Communication: X-ray technicians require communication skills to interact with patients, answer their questions, collaborate with team members and share important information with members of the patient's care team. Strong interpersonal communication skills also help you build trust and rapport with patients.
- Technical abilities: Using medical imaging machines to record accurate images of tissues, organs and bones requires specialised knowledge and training. These technical skills include knowing how to operate, maintain, clean, set up and troubleshoot issues with imaging equipment like x-ray machines, CT scanner.
- Medical knowledge: Having fundamental medical knowledge enables you to record clear images for a proper diagnosis. This includes a basic understanding of human anatomy, knowledge of medical terminologies and emergency skills, such as cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
- Teamwork: X-ray technicians work in a team with other diagnostic experts, nurses, doctors, surgeons and medical professionals. Being able to follow instructions from senior members of the team, manage patient information and collaborate with others to ensure test accuracy, and patient safety are valuable skills.
- Attention to detail: This role often involves working in a high-pressure and dynamic work environment, and paying attention to detail while using complex machinery is key. This includes performing all safety protocols, ensuring image accuracy and maintaining patient records.
- Time management: The work pressure in a large hospital or diagnostic centre can be high, as the role may require you to tend to many patients in a day. Knowing how to manage your time, schedule and prioritise tests, and work efficiently helps you to meet deadlines.





User's Comments
No comments there.